ASTALAVISTA! Why Is Elasticity 1 At Revenue Maximizing Price
On the other hand an increase in price. Both revenue and profit will fall with price decreases.

Pdf Making Price Elasticity A Useful Metric For Maximizing Profit
In the red part of the curve prices are below the revenue-maximizing price.

Why is elasticity 1 at revenue maximizing price. Price elasticity relates with total revenue gained when price increases or decreases. B Price elasticity of the demand is known to be -25 and the firm lowers the prices by 5. Revenue Versus Profit Considerations.
If elasticity is 1 the total revenue is already maximized and you would advise that the company maintain its current price level. And at that price the elasticity of demand is exactly 1. If the elasticity is greater than 1 it means a larger change in quantity for a smaller change in price so lowering the price raises profits.
This formula only works if demand is elastic. C Price elasticity of the demand is known to be 1 and the firm raises the prices by 1. 2 MC 1 2 MC 1 2 2 MC p So the profit maximizing price will be two times the marginal cost.
Revenue Quantity x Price Unit elasticity Price Elasticity of Demand of -1 Elasticity of Demand Change in Quantity Change in Pric. Khan Academy is a 501c3 nonprofit organization. Increases in price will offset the decrease in number of units sold but increase your total revenue.
TOTAL REVENUE AND PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND. You want to adjust your price until your elasticity of demand number is -1 or 1 if you use absolute value. See some everyday examples.
This means your books are elastic. To see why imagine that demand is inelastic. In terms of revenues your 8 dollar books will generate 1200 in revenue.
Decreasing output would reduce costs and. Elasticity measures the degree to which the quantity demanded responds to a change. Total revenue is price times the quantity of tickets sold TR P x Qd.
In this case youll get -18. If the elasticity were 06 then you would advise the company to increase its price. TOTAL REVENUE PRICE PER UNIT OF GOOD QUANTITY OF GOOD SOLD.
Answer 1 of 2. Now you can plot out how much you can increase revenues through discounts. Multiply values to yield a price of 800.
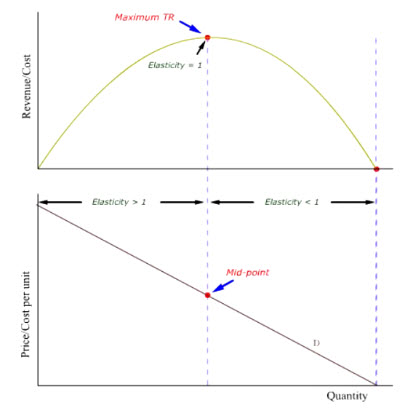
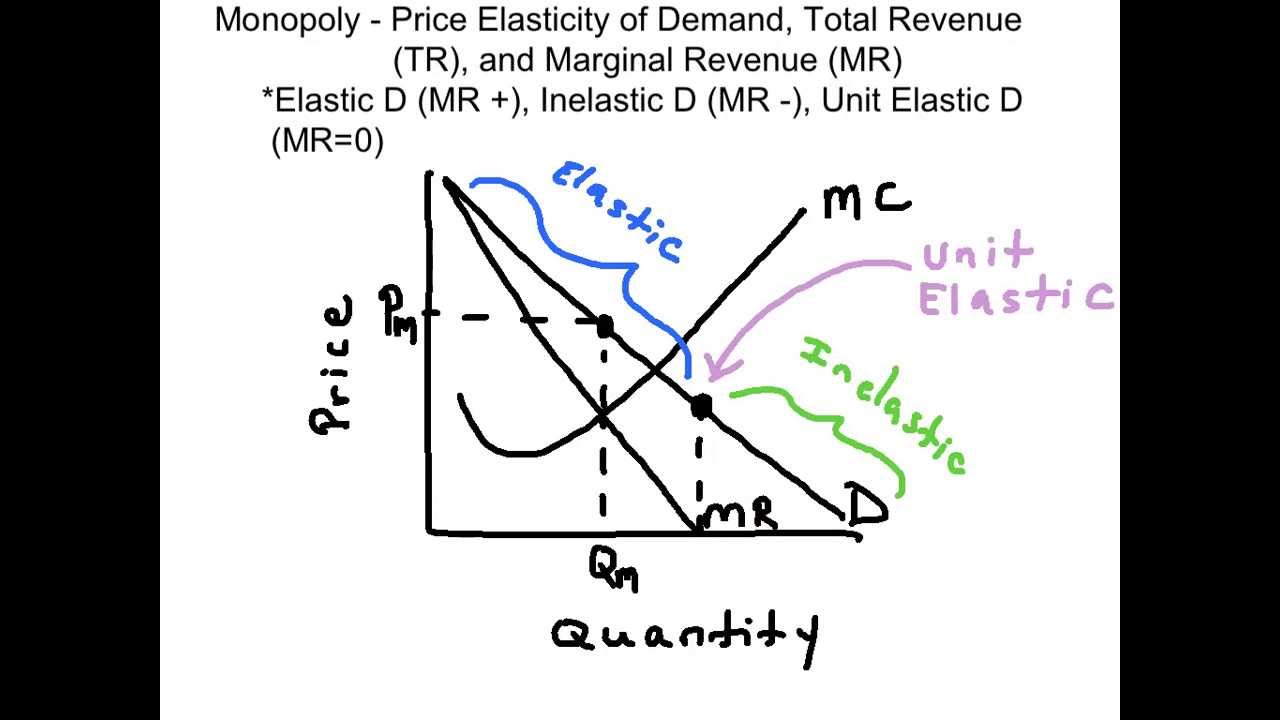
Consequently why is elasticity 1 at the revenue maximizing price. When the elasticity is less than one represented above by the blue regions demand. C If demand is perfectly inelastic then revenue is the same at any price.
What is the intuition for why elasticity is 1 at the revenue-maximizing price. A total revenue test approximates price elasticity of demand by measuring the change in total revenue from a change in the price of a product or service. Learn what cross price elasticity of demand means.
If we decrease prices elasticity drops below 1 thus the demand does not increase enough to compensate. If you get back an elasticity of demand number less than -1 or greater than 1 if you use absolute value then decrease your price and your revenue should increase. The demand curve in Panel c has price elasticity of demand equal to 100 throughout its range.
There are many ways a firm can increase its total revenue. Elasticity measures the degree to which the quantity demanded responds to a change in price. It can be calculated by multiplying the price per unit of a good by the quantity sold.
The key concept in thinking about collecting the most revenue is the price elasticity of demand. In order to determine the profit-maximizing price you follow these steps. The three possibilities are laid out in Table 1.
Imagine that the band starts off thinking about a certain price which will result in the sale of a certain quantity of tickets. Guessing that this question is based on intro to Micro so not using calculus and over simplified Let us start with some definitions. Revenue-Maximizing Prices and Demand Elasticity.
B If demand is price elastic then decreasing price will increase revenue. This is also where elasticity is precisely equal to 10. Your company produces a good at a constant marginal cost of 600.
As those two variables interact they can have an impact on a firms total revenue. This concept is useful to fix price that maximizes revenues. Empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in Panels c and d that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve.
A Price elasticity of the demand is known to be -05 and the firm raises the price by 10. Price elasticity of demand describes how changes in the price for goods and the demand for those same goods relate. -If the price elasticity of demand equals 1 a rise in price causes no change in revenue for the seller.
D Elasticity is constant along a linear demand curve and so too is revenue. The price elasticity of demand for the good is 40. When the elasticity of demand is greater than one represented above by the purple regions demand is considered elastic and lowering the price leads to an increase in revenue.
Revenue is the amount of money a firm brings in from salesie the total number of units sold multiplied by the price per unit. -1 is the point of unit elastic. This means that for every one percent decrease in price demand will increase by 18 percent.
1 MR p 1 MR MC So if the price elasticity of demand is 2 the profit maximizing price is. Calculate the value in the parentheses. Revenues are maximized when the price is 50exactly halfway down the demand curve.
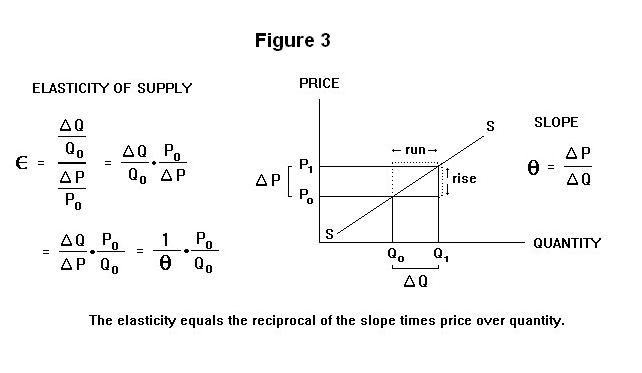
- If elasticity is greater than 1 and the supply curve shifts to the left price will rise. Total revenue is the total income that a company receives from selling goods. Therefore while it may be appealing to think about the relationship between price and revenue especially since the concept of elasticity makes it easy to do so its only a starting.
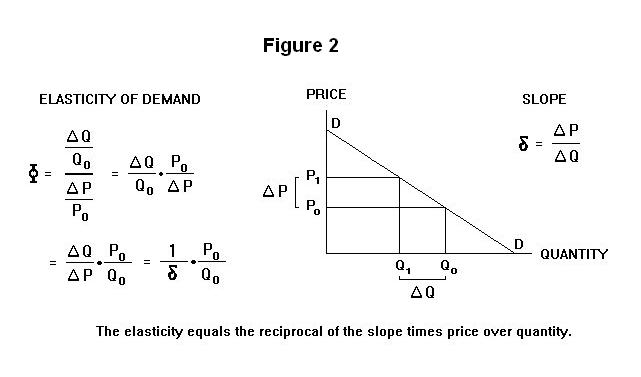
In Panel d the price elasticity of demand is equal to 050 throughout its range. More What Does Elasticity Mean. The elasticity of a demand curve is the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
A If demand is price inelastic then increasing price will decrease revenue. Determinants of price elasticity and the total revenue rule Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to anyone anywhere. Substitute 600 for MC and 40 for ç.
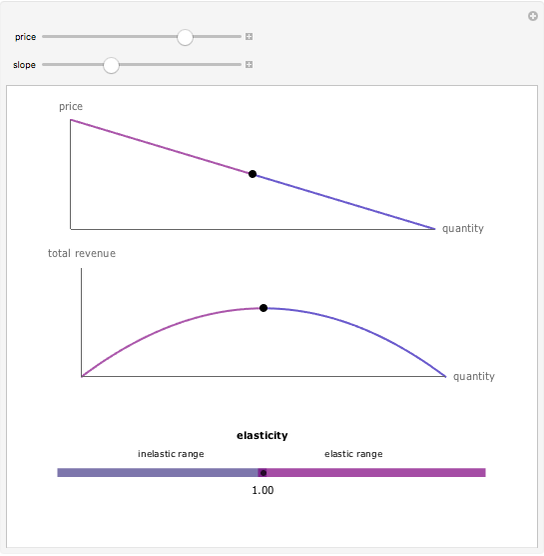
Intro Price Elasticity of Demand Other Elasticities Revenue Midpoint Formula Elasticity Elasticity and Revenue It turns out the price and quantity corresponding to the unit elastic portion of the demand curveIs also the revenue maximizing price and quantity. Find out why business owners and economists like to know cross price elasticity and discover how to calculate it. If the firm is producing at the point where demand is unit elastic it has maximized revenue and any changes in output will.
Economically speaking the goal of a company is to maximize profit and maximizing profit is not usually the same thing as maximizing revenue. Now you probably noticed something very interesting while playing with the graph.
Elasticity Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue
Price Elasticity Of Demand And Total Revenue Course Hero

Price Elasticity Of Demand Economics Online
Living Economics Demand Elasticity And Total Revenue Youtube Transcript
Elasticity Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue
Elasticity Total Revenue And The Linear Demand Curve Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Price Elasticity Of Demand Boundless Economics
Elasticity Of Demand Marginal Revenue Youtube

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics
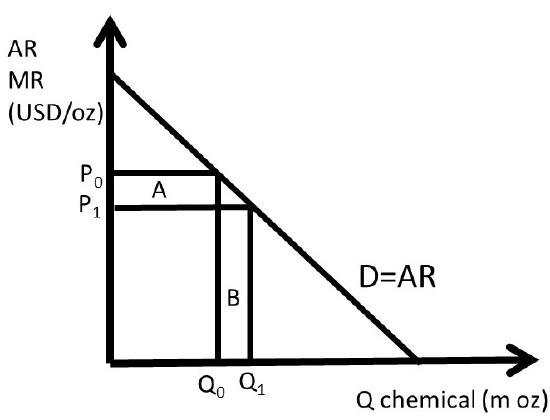
3 3 Marginal Revenue And The Elasticity Of Demand Social Sci Libretexts

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics
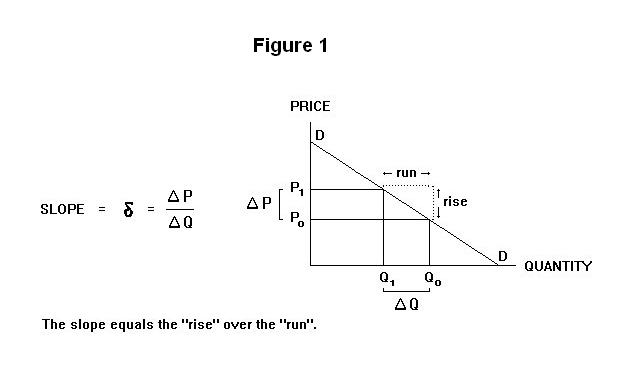
Elasticity Total Revenue And Marginal Revenue

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics
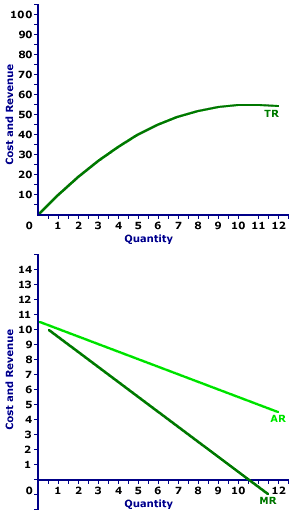
Amosweb Is Economics Encyclonomic Web Pedia

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics

4 2 Elasticity And Revenue Principles Of Microeconomics

Comments
Post a Comment